What is a Stool Test? A Comprehensive Guide
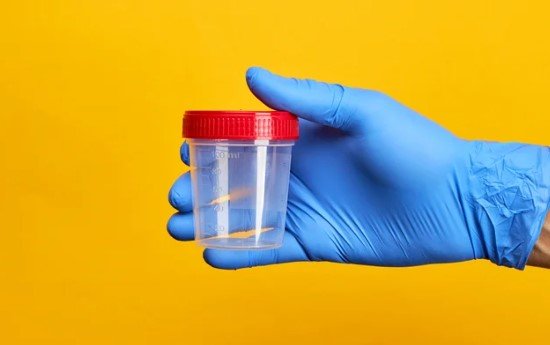
A stool test is an important diagnostic test that provides a comprehensive overview of the digestive system. The stool sample examined could range from infections through food intolerances to chronic morbidities and can even detect early signs of cancer. Since stool tests are non-invasive and highly diagnostic, they make up an important part of modern medical practice.
If stool tests hold promise as a primary mode for preventive medicine, that can be proven by the understanding that those tests are very reliable not only for conditions already existing but also in providing an overview of the whole gut microbiome and a vital part of your immune system and general health as the biology understands it. Now, let’s understand how the stool test works and when you’ll probably need one.
What is a Stool Test?
The stool test is a laboratory investigation of fecal specimens that identifies gastrointestinal disorder-causing conditions. This test is very effective in diagnosing infections, poor nutrient absorption, inflammations, and even parasites. It is most effective in identifying diseases that cannot be visualized through other means, making it most important for gastroenterologists and general health practitioners.
- Bacterial, viral, or parasite presence.
- Blood or mucus in the stool.
- Digestive enzymes and fats.
- The health and balance of microbiome.
A wide range of health problems are:
- Digestive disorders, e.g., Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
- Harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasite infections cause infectious diseases.
- Blood in stool indicates possible bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Malabsorption syndrome in which the body is not able to absorb nutrients.
Stool tests are made specifically for diagnostic purposes so that the results can be accurate and taken directly into treatment plans. That is why they are never out of place in healthcare, whether you are visiting with acute symptoms or habitual checkups.
Understanding the Procedure of a Stool Test
The stool test procedure is straightforward and non-invasive but usually involves the following steps:
- Sample Collection
The patients are handed a sterile container to collect their stool specimens. This container is a contamination-free collection and preserves the sample. Instructions are clear about how the specimen is to be collected; it should not include water, urine, or other materials.
- Preparation
Some tests may recommend that a patient avoid certain foods prior to the stool test. For example, when the test checks for blood in a stool sample, red meat, beets, or iron supplements would need to be avoided because they could cause false positives.
- Laboratory Analysis
The sample is sent away to the laboratory, where a series of tests is performed on it. These could include:
- Microscopic examination for parasite or egg detection.
- Chemical tests for the evidence of blood, bile, or fats in the sample are carried out.
- Culturing is used to identify an infection by growing the bacteria.
- Results and Interpretation
Once the results are obtained, medical professionals interpret them for diagnosis or further tests according to their recommendations. In most cases, it takes only a few days before receiving the results, but this may depend on the level of complexity.
Read also: The Benefits of Professional Urgent Care Services
7 Signs You Need to Take a Stool Test
There are times when our body shouts that our stool should be tested or even any other tests, for example, a cortisol test. The following are seven signs to take note of:
- Persistent Digestive Issues
Chronic diarrhea, constipation, or an abrupt shift in one’s bowel habits can indicate some underlying conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), infections, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). A fecal examination can help identify the cause and provide a requisite therapeutic regimen.
- Unexplained Weight Loss
If someone is experiencing weight loss with no change in diet or activity, it is a good indication that something may be wrong with the absorption mechanism, such as celiac disease or pancreatic insufficiency; stool investigation could, therefore, be useful in revealing why nutrients are not absorbable by the body.
- Visible Blood or Mucus in Stool
Blood or mucus in stool are signs of severe diseases like ulcers, Crohn’s disease, or colorectal cancer. Alongside these symptoms, blood can already be visible in the stool; however, a stool sample can collect even microparticles that are sometimes early indicators of gastrointestinal diseases.
- Frequent Abdominal Pain
More often, recurring pain or cramping in the abdomen may indicate some sort of infection, inflammation, or other gastrointestinal disorders. Usually, this symptom is kind of accompanied by other symptoms such as diarrhea or bloating, necessitating stool test.
- Exposure to Contaminated Water or Food
A stool test is not just a simple test, as it is a specialized medical procedure. A stool test helps identify any kind of infection, such as Salmonella, E. coli, or Giardia, which is usually caused by eating some sort of contaminated food or water. When you consume contaminated or certain types of food or water, you may experience symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, or fever; these indicate that you need to take a stool test to determine the root cause.
- Chronic Fatigue or Weakness
Sometimes, many individuals face nutritional deficiencies, which are the result of malabsorption of nutrients that cause excess fatigue to an individual. However, taking a cortisol test helps in investigating fatigue caused by cortisol imbalance, and it also identifies the digestive issues that contribute to energy depletion in the body. The issues may include chronic infections or fat malabsorption, which are found when the stool test is conducted.
- Travel to High-Risk Areas
Travelers to areas with unsafe sanitation could also be at risk of parasitic or bacterial diseases. Tests, such as stool tests, confirm whether the pathogens are Giardia or Cryptosporidium, which could help ensure timely treatment.
The Final Words
Stool tests are not merely diagnostic procedures; they also provide a better understanding of the overall status of health and that of the gut. A stool sample analysis allows the health care provider to determine conditions ranging from digestive disorders to infections, malabsorption syndromes, and chronic illnesses. Due to its noninvasiveness and diagnostic significance, stool tests are a tool of modern medicine.